How to loop this and do batch predictions for the entire images in folder with file name?
Document Details
⚠ Do not edit this section. It is required for docs.microsoft.com ➟ GitHub issue linking.
- ID: 754dd7d5-dd8b-4a75-5d79-0ba621a847cd
- Version Independent ID: 3cca3535-1c16-2da1-46c6-421cbf808bc3
- Content: Tutorial: Run TensorFlow model in Python - Custom Vision Service
- Content Source: articles/cognitive-services/Custom-Vision-Service/export-model-python.md
- Service: cognitive-services
- GitHub Login: @areddish
- Microsoft Alias: areddish
All 3 comments
@visuazn Thanks for the feedback. We are investigating into the issue and will update you shortly.
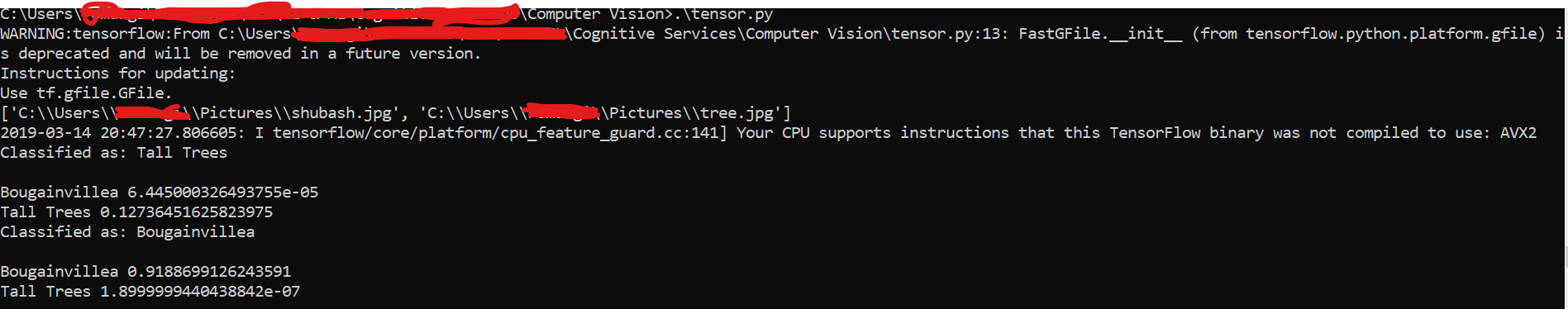
@visuazn Here is the same code of this tutorial using cv2 to predict all images in a folder. I have used my model to detect trees in the output screen shot attached.
Please update the path to your model, labels.txt and images folder.
pip install tensorflow
pip install pillow
pip install numpy
pip install opencv-python
import tensorflow as tf
import os
graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
labels = []
# Import the TF graph
with tf.gfile.FastGFile("path_to_model.pb", 'rb') as f:
graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read())
tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name='')
# Create a list of labels.
with open("path_to_labels.txt", 'rt') as lf:
for l in lf:
labels.append(l.strip())
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import cv2
import glob
# Load from a folder
imagePath = 'path_to_image_folder'
files = []
files.extend(glob.glob(imagePath + '*.' + 'jpg'))
print(files)
images_cv2 = [cv2.imread(file) for file in files]
images=[cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) for img in images_cv2]
#helper functions
def convert_to_opencv(image):
# RGB -> BGR conversion is performed as well.
r,g,b = np.array(image).T
opencv_image = np.array([b,g,r]).transpose()
return opencv_image
def crop_center(img,cropx,cropy):
h, w = img.shape[:2]
startx = w//2-(cropx//2)
starty = h//2-(cropy//2)
return img[starty:starty+cropy, startx:startx+cropx]
def resize_down_to_1600_max_dim(image):
h, w = image.shape[:2]
if (h < 1600 and w < 1600):
return image
new_size = (1600 * w // h, 1600) if (h > w) else (1600, 1600 * h // w)
return cv2.resize(image, new_size, interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
def resize_to_256_square(image):
h, w = image.shape[:2]
return cv2.resize(image, (256, 256), interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
def update_orientation(image):
exif_orientation_tag = 0x0112
if hasattr(image, '_getexif'):
exif = image._getexif()
if (exif != None and exif_orientation_tag in exif):
orientation = exif.get(exif_orientation_tag, 1)
# orientation is 1 based, shift to zero based and flip/transpose based on 0-based values
orientation -= 1
if orientation >= 4:
image = image.transpose(Image.TRANSPOSE)
if orientation == 2 or orientation == 3 or orientation == 6 or orientation == 7:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_TOP_BOTTOM)
if orientation == 1 or orientation == 2 or orientation == 5 or orientation == 6:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
return image
for imageFile in images:
#Not using PIL since we are using cv2
#image = Image.open(imageFile)
# Update orientation based on EXIF tags, if the file has orientation info.
image = update_orientation(imageFile)
# Convert to OpenCV format
image = convert_to_opencv(image)
# If the image has either w or h greater than 1600 we resize it down respecting
# aspect ratio such that the largest dimension is 1600
image = resize_down_to_1600_max_dim(image)
# We next get the largest center square
h, w = image.shape[:2]
min_dim = min(w,h)
max_square_image = crop_center(image, min_dim, min_dim)
# Resize that square down to 256x256
augmented_image = resize_to_256_square(max_square_image)
# Get the input size of the model
with tf.Session() as sess:
input_tensor_shape = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name('Placeholder:0').shape.as_list()
network_input_size = input_tensor_shape[1]
# Crop the center for the specified network_input_Size
augmented_image = crop_center(augmented_image, network_input_size, network_input_size)
# These names are part of the model and cannot be changed.
output_layer = 'loss:0'
input_node = 'Placeholder:0'
with tf.Session() as sess:
prob_tensor = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name(output_layer)
predictions, = sess.run(prob_tensor, {input_node: [augmented_image] })
# Print the highest probability label
highest_probability_index = np.argmax(predictions)
print('Classified as: ' + labels[highest_probability_index])
print()
# Or you can print out all of the results mapping labels to probabilities.
label_index = 0
for p in predictions:
truncated_probablity = np.float64(np.round(p,8))
print (labels[label_index], truncated_probablity)
label_index += 1
Screen shot of output of script.
We will now proceed to close this thread. If there are further questions regarding this matter, please tag @RohitMungi-MSFT in your reply. We will gladly continue the discussion and we will reopen the issue.
Thanks. Great
Most helpful comment
@visuazn Here is the same code of this tutorial using cv2 to predict all images in a folder. I have used my model to detect trees in the output screen shot attached.
Please update the path to your model, labels.txt and images folder.
Screen shot of output of script.
We will now proceed to close this thread. If there are further questions regarding this matter, please tag @RohitMungi-MSFT in your reply. We will gladly continue the discussion and we will reopen the issue.