Vision: Error using sequential on faster-rcnn to get regional proposal network object features
I’m trying to use pretrained FasterRCNN network provided in torchvision.
model=torchvision.models.detection.fasterrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
model([image_tensor])
working perfectly fine but when I use sequential to stop at intermediate layers like this
model2=nn.Sequential(*list(model.children())[:-2])
to use until RPN network I’m getting error when passing a image as show below
TypeError: conv2d(): argument 'input' (position 1) must be Tensor, not tuple
So then, I tried to inherit nn.module and implement based on Generalized RCNN and faster-rcnn.py as shown here but instead of Kx2048 features I'm getting 862x4. feature vector.
All 19 comments
The trick model2=nn.Sequential(*list(model.children())[:-2]) doesn't work for all types of models, and in particular won't work for faster-rcnn.
The output of the RPN returns a list of proposals, which are in the format [N, 4], as you obtained.
What are you looking to obtain instead? The activation maps?
I'm sorry if my understanding of network is wrong but I'm looking to obtain object-centric image features (output of region proposal network) whose size is 2048xK which functions as pre-trained features for VQA. Reference to paper bottom-up
You might want to get the output of the roi_pool from the roi_heads, which gives you, for each proposal, the cropped feature maps at the locations specified by the proposals. Then, you can apply your network to those cropped features to obtain your encodings
Thanks @fmassa . It worked now I am able to get all top features and subselect on them. One last piece advice, As I see I followed different approach to build model, I am guessing loading state dict would be different than usual. If its that case, is there any resource I can follow to load the model later from state dict. Thanks
One easy option is to load the full pre-trained model, and pass to your class the attributes of this model. Might be the simplest approach
Sure. Thanks so much 👍 💯
No worries! Let us know if you have any other comment / feedback
Hi @fmassa
How can I get the output of the roi_pool?
@YoussefSaadYoussef one easy way is to add a hook to get the output
outputs = []
hook = model.roi_heads.box_roi_pool.register_forward_hook(
lambda self, input, output: outputs.append(output))
res = model(inputs)
hook.remove()
print(outputs[0])
Thanks a lot for your response @fmassa
the hook returned 1000 region proposals but I would like to return the features only for the regions or boxes which selected at the end. specifically the mean-pooled convolutional features from these regions which have dimension D of 2048
In this case, I would recommend adding the hook in the model.backbone, and then computing the pooling yourself. Something like
outputs = []
hook = model.backbone.register_forward_hook(
lambda self, input, output: outputs.append(output))
res = model(inputs)
hook.remove()
selected_rois = model.roi_heads.box_roi_pool(
outputs[0], [r['boxes'] for r in res], [i.shape[-2:] for i in inputs])
print(selected_rois)
Thanks much @fmassa your solution works so well for me. I used this in my application and am posting here your code wrapped as a function for any one who may have a similar requirement:
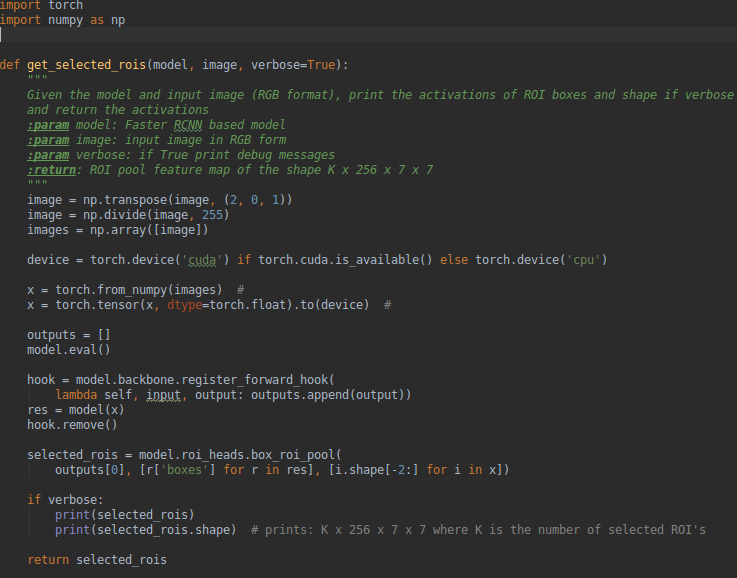
Great @ananthpn let us know if you have further questions
Hi
I am dealing with the same issue and I am trying to get the 2048 vector representations out of this pre-trained model. I used the code you introduced here to get the ROIs but I am wondering how to get the actual representations with this approach. Can you help me @fmassa?
@hfaghihi15 which 2048 vector representation are you talking about? It all depends on which layer of the model you want to get it from, and with the approach pasted by @ananthpn you can get the output of any layer that you want
Hi @fmassa
How am I supposed to get top-K features from the 1000-feature feature map from roi_pool? Thx
The solution from https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/1001#issuecomment-589532923 probably do what you want
The solution from #1001 (comment) probably do what you want
Thank you!
In this case, I would recommend adding the hook in the
model.backbone, and then computing the pooling yourself. Something likeoutputs = [] hook = model.backbone.register_forward_hook( lambda self, input, output: outputs.append(output)) res = model(inputs) hook.remove() selected_rois = model.roi_heads.box_roi_pool( outputs[0], [r['boxes'] for r in res], [i.shape[-2:] for i in inputs]) print(selected_rois)
Hey @fmassa, I need one clarification. Based on your code, does this mean that the outputs (region proposals) from the RegionProposalNetwork are in the original image sizes? Because in your code snippet, you provide the proposals in the original image size, i.e., the predicted and postprocessed ones, to the box_roi_pool module. I also had a look at the docstring of the forward method of MultiScaleRoIAlign and it states that
boxes (List[Tensor[N, 4]]): boxes to be used to perform the pooling operation, in
(x1, y1, x2, y2) format and in the image reference size, not the feature map
reference.
which raises the question, what reference image sizes? (1) The ones before GeneralizedRCNNTransform (original image sizes), or (2) the ones after GeneralizedRCNNTransform? Your code snippet is inline with (1). On the other hand, on #1477 (comment) you mentioned
the boxes should be in the same format as what we consider in the RPN
which in that context seem to be inline with (2), i.e., the size of the images after GeneralizedRCNNTransform. Please let me know in case I need to be more specific. @ananthpn what was your experience with this?
Most helpful comment
Thanks much @fmassa your solution works so well for me. I used this in my application and am posting here your code wrapped as a function for any one who may have a similar requirement: