Vagrant: error while vagrant up,can not connect box
I tried to use the vagrant in my server(centos6.7) without gui. I encountered some problem.
This is how I start the service.
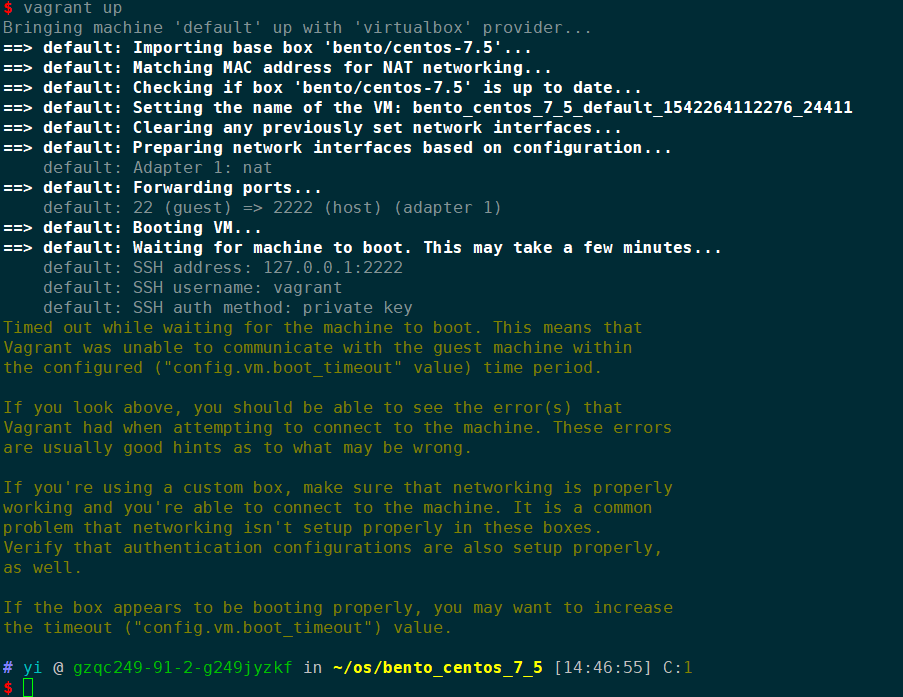

How can I solve this problem? I am tired of configure the development environment again and again.
All 21 comments
Hi there,
Thank you for opening an issue. However, there is not enough information here to reproduce or provide a recommendation. When you first open an issue, a template is pre-filled in the box. That template provides instructions for getting your host and guest information, the version of Vagrant, and the debug output. Without that information, it is very challenging for us to assist you.
Please supply that information either by updating this ticket or by closing this ticket and opening a new one. Thank you!
Vagrant version
$ vagrant -v
Vagrant 2.2.1
Host operating system
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.7 (Final)
Guest operating system
CentOS release 7.5 (bento/centos-7.5)
Vagrantfile
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "bento/centos-7.5"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end
Debug output
Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> default: Checking if box 'bento/centos-7.5' is up to date...
==> default: Clearing any previously set forwarded ports...
==> default: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> default: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
default: Adapter 1: nat
==> default: Forwarding ports...
default: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> default: Booting VM...
==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
default: SSH username: vagrant
default: SSH auth method: private key
Timed out while waiting for the machine to boot. This means that
Vagrant was unable to communicate with the guest machine within
the configured ("config.vm.boot_timeout" value) time period.
If you look above, you should be able to see the error(s) that
Vagrant had when attempting to connect to the machine. These errors
are usually good hints as to what may be wrong.
If you're using a custom box, make sure that networking is properly
working and you're able to connect to the machine. It is a common
problem that networking isn't setup properly in these boxes.
Verify that authentication configurations are also setup properly,
as well.
If the box appears to be booting properly, you may want to increase
the timeout ("config.vm.boot_timeout") value.
Expected behavior
vagrant ssh work.
Actual behavior
vagrant ssh failed.
ssh_exchange_identification: Connection closed by remote host
Steps to reproduce
1.vagrant box add bento/centos-7.5
- vagrant init bento/centos-7.5
- vagrant up
- vagrant ssh
@PraflyGod Please provide a gist which contains the output from:
vagrant up --debug
This will provide us with more information and aid us in helping to determine what the underlying cause may be. Thanks!
I have the same problem. Vagrant 2.2.1 with a Red Hat 7.6 custom box.
This is the output of vagrant up --debug: https://gist.github.com/asandroq/fe841e830c022a6155e996bf878e2043
I met the same problem.
- uninstall vagrant.
- install 2.2.0
- vagrant up (create vm)
- vagrant halt
- vagrant up (debug_220.log)
- vagrant halt
- upgrade to vagrant 2.2.1
- vagrant up (debug_221.log)
https://gist.github.com/hirayama-onagigawa-computing/694bdcaf005bba32c56da7b0a6e67442
Is this correct?
-nictype1="82540EM"
+nictype1="virtio"
Had the same issue after upgrading to Vagrant 2.2.1
It seems that that NIC type is influencing device names, which causes the initial DHCP request for the primary NIC to fail.
Work-around appears to be this:
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.default_nic_type = nil
end
This avoids the problem and existing vms can be booted.
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.default_nic_type = "82540EM"
end
Had the same issue and eventually worked out the same fix as above. I suspect this has been caused by #10383. This explicitly sets the NIC type to virtio.
Any boxes built with Packer would, by default, have been built using the default NIC type of '82540EM' - the Virtualbox default.
As @MarkSummers has pointed out, the change between the device type used when building the box (82540EM) and the device type used when running the box with Vagrant (virtio) is causing a difference in the predictable device name for the NIC. On my CentOS box I get the following:
Nov 17 16:29:52 localhost /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-eth: Device enp0s3 does not seem to be present, delaying initialisation.
If I explicitly set the NIC type to nil or 82540EM (same thing) the machine and networking comes up fine.
Clearly it's possible to work around the disparity. However, I suspect Packer and Vagrant need to be using the same default NIC type to avoid this issue altogether.
Interesting. I had tested the default nic type modification on a large number of guests to find any adverse affects and had not seen this behavior. I am also debugging DHCP issues with the default NAT device where the device is brought up but no leases are offered.
By default in packer the default nic type is chosen by vbox, and with the default_nic_type set to nil, that is the result from Vagrant as well. The addition of the new configuration option (and enabling a default value) was applied in response to the vulnerability within the e1000 implementation. I'll have a closer look at this today and get a patch release out if required.
@chrisroberts Just in case(!!)... be aware that the bento/debian boxes disable predictable device names for networking and default to using 'eth0' (see HERE). As such you wouldn't see this issue testing with that box or similar ...
I don't know why the same hasn't been done with the CentOS boxes.
still not work for me.
@PraflyGod Did you destroy and re-add your box? The problem seems to occur during initial import, so provisioning isn't enough.
re-add? You means vagrant box add? Is it necessary? I tried to destroy and vagrant up again. And we got this.
https://gist.github.com/PraflyGod/c3d4b8beaa582722b101ea03aa6b5ea5
This is the vagrant file I used.
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
# All Vagrant configuration is done below. The "2" in Vagrant.configure
# configures the configuration version (we support older styles for
# backwards compatibility). Please don't change it unless you know what
# you're doing.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
# The most common configuration options are documented and commented below.
# For a complete reference, please see the online documentation at
# https://docs.vagrantup.com.
# Every Vagrant development environment requires a box. You can search for
# boxes at https://vagrantcloud.com/search.
config.vm.box = "bento/centos-7.5"
# Disable automatic box update checking. If you disable this, then
# boxes will only be checked for updates when the user runs
# `vagrant box outdated`. This is not recommended.
# config.vm.box_check_update = false
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine. In the example below,
# accessing "localhost:8080" will access port 80 on the guest machine.
# NOTE: This will enable public access to the opened port
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
# Create a forwarded port mapping which allows access to a specific port
# within the machine from a port on the host machine and only allow access
# via 127.0.0.1 to disable public access
# config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080, host_ip: "127.0.0.1"
# Create a private network, which allows host-only access to the machine
# using a specific IP.
# config.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.10"
# Create a public network, which generally matched to bridged network.
# Bridged networks make the machine appear as another physical device on
# your network.
# config.vm.network "public_network"
# Share an additional folder to the guest VM. The first argument is
# the path on the host to the actual folder. The second argument is
# the path on the guest to mount the folder. And the optional third
# argument is a set of non-required options.
# config.vm.synced_folder "../data", "/vagrant_data"
# Provider-specific configuration so you can fine-tune various
# backing providers for Vagrant. These expose provider-specific options.
# Example for VirtualBox:
#
# config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
# vb.memory = "1024"
# end
#
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.default_nic_type = "82540EM"
end
# View the documentation for the provider you are using for more
# information on available options.
# Enable provisioning with a shell script. Additional provisioners such as
# Puppet, Chef, Ansible, Salt, and Docker are also available. Please see the
# documentation for more information about their specific syntax and use.
# config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
# apt-get update
# apt-get install -y apache2
# SHELL
end
@PraflyGod It was necessary for me when using custom CentOS box images. I see now that you are using the Bento box.
@DanHam I was under the impression that the latest Bento CentOS box is also fixing the interface names to be eth0 etc. See https://github.com/chef/bento/issues/1113 and https://github.com/chef/bento/blob/master/centos/http/7/ks.cfg
@PraflyGod I tested your Vagrantfile with no changes and it is working here.
@Womagrid Ah... OK. Thanks for pointing that out. I was wondering why they hadn't done the same thing for CentOS that they had done for Debian. I had a quick skim through the scripts for CentOS and couldn't see anything related to disabling predictable device names for networking. Clearly they've done this via the kickstart instead.
This should mean that the differences between the default NIC type in Packer and Virtualbox for the bento boxes should not have any affect. By way of confirmation, I was able to run the bento/centos-7.5 box without issue. This should only affect boxes that retain the default behaviour of 'predictable device names' for network devices.
Most likely the issue @PraflyGod is seeing is being caused by something else.
For completeness:
OS: Mac OS X 10.11.6 15G22010
Virtualbox: 5.2.22r126460
Vagrant: 2.2.1
Vagrant plugins:
- vagrant-aws (0.7.2, global)
- vagrant-google (2.2.1, global)
- vagrant-reload (0.0.1, global)
- vagrant-share (1.1.9, global)
- vagrant-vmware-desktop (2.0.1, global)
The release today (2.2.2) will resolve this issue. It includes #10450 that updates the default_nic_type behavior. More information can be found in #10448 as well.
Cheers!
The release doesn't solve my problem. The problem is that I tried to vagrant up in cloud service(tencent cloud). So the question is that how to vagrant up in nested virtualization(most cloud service)
@PraflyGod Nested virt generally isn't available on cloud services. The best you'll be able to do is using the docker provider.
I tried to use the vagrant in my server(centos6.7) without gui. I encountered some problem.
This is how I start the service.
How can I solve this problem? I am tired of configure the development environment again and again.
Hi , I am also getting same issue with vagrant up
did you find the solution for this problem? if yes please share with me too.
Thanks
I'm going to lock this issue because it has been closed for _30 days_ ⏳. This helps our maintainers find and focus on the active issues.
If you have found a problem that seems similar to this, please open a new issue and complete the issue template so we can capture all the details necessary to investigate further.
Most helpful comment
This avoids the problem and existing vms can be booted.