Terminal: Calling wt from cmd for working directory "C:\" causes an error
Hi,
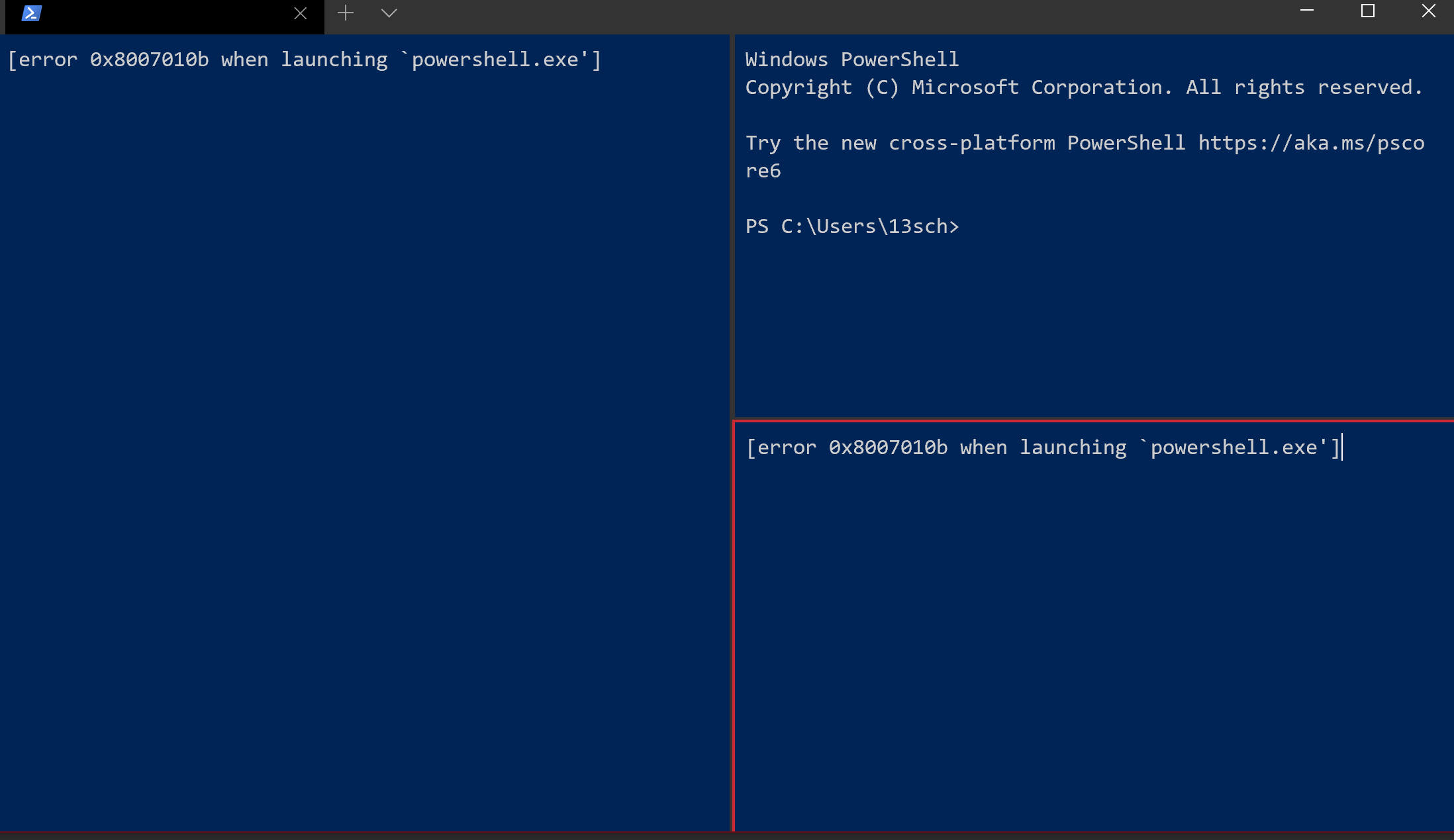
I was testing the new command line options to open a Windows Terminal for a specified working directory. When calling wt new-tab -d "C:\" from PowerShell this seems to work. Calling the same command from cmd however will print the error message [error 0x8007010b when launchingpowershell.exe']` in the newly opened Windows Terminal instance. Using the "-p" option to launch a different shell will provoke the same error message for the executable associated with the specified profile name.
Environment
Windows build number: Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.18363.657]
Windows Terminal version: 0.9.433.0
Steps to reproduce
Call wt new-tab -d "C:\" from cmd.
Expected behavior
Open a new Windows Terminal tab with path C:\ set as the current working directory.
Actual behavior
Opens a Windows Terminal instance with the message:
[error 0x8007010b when launching `powershell.exe']
All 22 comments
Interesting. It looks like we're not handling quotes properly when there _aren't_ spaces.
Unfortunately this is the default behavior if the command line gets tokenized to argv. This is unrelated to spaces in the path. The backslash just escapes the double quote and thus, it's treated as literal character. Also CommandLineToArgvW behaves the same.
You could escape the backslash with another backslash to make it work again like wt new-tab -d "C:\\".
If we want to fix that we would need to establish our own command line tokenization.
Yeah had the same error when using this command wt -d C:\Users\cinnamon\GitHub\WindowsTerminal ; split-pane -p "Command Prompt" ; split-pane -p "Ubuntu" -d \wsl$\Ubuntu\home\cinnak -H
You must know that your username is not cinnamon, right?
Yes, but that's not the issue here
What else is the issue then? You call it with a non-existing user profile and with wsl$ which certainly should have been rather $wsl (but which I wouldn't expect to get expanded to a value in a Windows command line).
(Actually, wsl$ is correct here. "cinnamon" and "cinnak" are not correct.)
It also looks like you don't even have a profile named Ubuntu.
Kayla's example was an _example_, not something that you can just run out of nowhere. You need to have a "command prompt" profile and an "ubuntu" profile, and the directories she's listed in the arguments, for it to work the same way.
You may benefit from the command line arguments documentation.
Similarly I'm trying to set a context menu shortcut via registry to open terminal from a folder's background context menu. I used to do this successfully with cmder by setting the command to "c:\path\to\cmder.exe" /START "%V".
Trying this with "C:\Users\krage\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\wt.exe" --startingDirectory "%V" shows the same 0x8007010b error when the path is the root of a lettered drive. It seems to work for other paths though with or without contained spaces, eg. C:\Windows and C:\Program Files both succeed.
I tried changing the command to "C:\Users\krage\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\wt.exe" powershell.exe -NoExit -Command Set-Location -LiteralPath "%V". Using this in the root of a drive doesn't generate an error but fails to change the path, the powershell session just winds up in the default starting directory of the default terminal profile. Paths without spaces eg. C:\Windows change directory successfully. Powershell shows an error for paths with spaces eg. C:\Program Files gives an error like this as though the quotes around the path didn't survive:
Set-Location : A positional parameter cannot be found that accepts argument 'Files'.
At line:1 char:1
+ Set-Location -LiteralPath C:\Program Files
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (:) [Set-Location], ParameterBindingException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : PositionalParameterNotFound,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.SetLocationCommand
As a quick hack for %V, you might be able to use.. hmm. "%V\."?
(Actually,
wsl$is correct here. "cinnamon" and "cinnak" are not correct.)
It also looks like you don't even have a profile named Ubuntu.Kayla's example was an _example_, not something that you can just run out of nowhere. You need to have a "command prompt" profile and an "ubuntu" profile, and the directories she's listed in the arguments, for it to work the same way.
You may benefit from the command line arguments documentation.
I have it working with a userprofile of Ubuntu-18.04, but what I'm wondering is what the error as described in the issue is coming from, [error 0x8007010b when launchingpowershell.exe']`
You're getting that error because you have a specified a working directory (with -d) that does not exist.
Awesome, thank you, fixed

As a quick hack for %V, you might be able to use.. hmm.
"%V\."?
Thanks, this seems this works everywhere I've tried so far.
Triaged this into 1.0; we should see if there's something we can do about it.
Triaged this into 1.0; we should see if there's something we can do about it.
I can take this and solve it along with #4170. I recall that I already have a piece of code to parse the command line somewhere in my snippet collection. Likely still in C though.
@zadjii-msft Do you think we need an alternative way to preserve literal quotes in the arguments? Or would it be OK to have them removed after tokenization? From what I see in the docs I'd guess it's save to strip them all.
(Sorry I deleted my comment earlier.)
I personally think that the terminal should stay consistent with other apps and use the standard CommandLineToArgvW.
Should we really fix this in the terminal? Is this not cmd.exe/Powershell's own problem? Other apps behave like this as well:
Powershell:
PS C:\Users\gregd> git "hello\" world
git: 'hello\' is not a git command. See 'git --help'.
cmd:
C:\Users\gregd>git "hello\" world
git: 'hello" world' is not a git command. See 'git --help'.
It looks like cmd.exe just passes the whole command line to the app while powershell parses the command line with its own rules and then escapes the arguments to recreate a command line. In particular, powershell doesn't care about backslashes so "C:\" is parsed as an argument with value C:\ which is then correctly escaped for CommandLineToArgvW. But cmd.exe just gives the command line as-is so "C:\" gets parsed as C:".
Is this not cmd.exe/Powershell's own problem?
Good point @greg904. But it doesn't behave the same in all shells and unfortunately it's not only a problem of the CMD. It fails from within the Run dialog and it fails also from a shortcut.
However, I just try to fix this in my PR because it has been accepted as an issue ...
was struggling with "%V" on command line and seems it need escapes too: \"%V\"
so ended up on this "Terminal window cmd" command on shell shortcut - if any help...
@="PowerShell -windowstyle hidden -Command \"Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/c start wt -p cmd -d \"%V\"'\""
Just to confirm, you are starting powershell, to start cmd, to start WT, to start powershell.
Why is your invocation three commands when just one would be fine? That’s crazy.
I've been using these context menu shortcuts:
(https://www.tenforums.com/tutorials/60132-open-bash-window-here-administrator-add-windows-10-a.html)](https://www.tenforums.com/tutorials/60132-open-bash-window-here-administrator-add-windows-10-a.html)
to be able to easy open "Open command/bash window here as administrator"
but I've not found any hint on how to create the same for Windows Terminal?
Actually there are still two more escapes missing from \"%V\" because this doesn't put the "" around path name and also when using shortcut on top of the Drive it requires the \. ending, so this works for all (Directory-Background/-shell/Drive/LibraryFolder):
@="PowerShell -windowstyle hidden -Command \"Start-Process cmd -Verb RunAs -ArgumentList '/c start wt -p cmd -d \"\"%V\\.\"\"'\""
@3col is there any reason you can’t just use wt.exe /d "%V\." instead of launching THREE DIFFERENT SHELLS AT ONCE
I see: you want the runas verb. Hm.
Most helpful comment
As a quick hack for %V, you might be able to use.. hmm.
"%V\."?