Salt: Issue with grains virtual in fluorine
Hi
I am currently testing flourine in one of our internal formulas, and running into an issue.
I originally thought it may be the underlying operating system of the CI server, but it doesn’t seem like it. The CI servers have been re-installed from CentOS and are now ubuntu 18.04.1, and are KVM VMs, (i.e. all identical).
In my formula I have a test {% if grains['virtual'] == "physical" %} and this is passing, which is shouldn’t. This test only passes in the centos docker containers and therefore running states that are meant for physical machines. However, this test does not pass in the Ubuntu docker containers, so doesn’t run the states meant for physical machines.
So in my CI pipeline, everything passes except for centos 6/7 with salt flourine.
My setup involves doing CI using kitchen-salt, under GitLab CI.
Below is a snippet of my .kitchen.yml, with any specifics removed
---
driver:
name: docker
platforms:
- name: centos-6
driver_config:
image: registry.ocf.co.uk/salt/docker/centos-6-kitchen:base
privileged: True
run_command: /sbin/init
use_cache: False
remove_images: True
provisioner:
salt_yum_repo: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/$releasever/$basearch/%s'
salt_yum_rpm_key: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/6/x86_64/latest/SALTSTACK-GPG-KEY.pub'
salt_install: yum
pip_bin: pip2.7
salt_bootstrap_options: "-P -p git -p curl -p sudo -y -x python2.7 git %s"
- name: centos-7
driver_config:
image: registry.ocf.co.uk/salt/docker/centos-7-kitchen:base
privileged: True
run_command: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd
use_cache: False
remove_images: True
provisioner:
salt_yum_repo: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/$releasever/$basearch/%s'
salt_yum_rpm_key: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/7/x86_64/latest/SALTSTACK-GPG-KEY.pub'
salt_install: yum
- name: ubuntu-16.04
driver_config:
image: registry.ocf.co.uk/salt/docker/ubuntu-16.04-kitchen:base
privileged: True
run_command: /lib/systemd/systemd
use_cache: False
remove_images: True
provisioner:
salt_apt_repo: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/apt/ubuntu/16.04/amd64'
salt_apt_repo_key: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/apt/ubuntu/16.04/amd64/latest/SALTSTACK-GPG-KEY.pub'
salt_install: apt
provisioner:
name: salt_solo
formula: <snip>
salt_install: bootstrap
salt_version: latest
salt_bootstrap_options: -P -p git -p curl -p sudo git %s
vendor_path: srv/salt
<SNIP>
suites:
- name: nitrogen
provisioner:
salt_version: '2017.7'
- name: carbon
provisioner:
salt_version: '2016.11'
- name: oxygen
provisioner:
salt_version: '2018.3'
- name: flourine
provisioner:
salt_version: '2019.2'
salt_install: bootstrap
- name: develop
provisioner:
salt_version: 'develop'
salt_install: bootstrap
below is an image of my pipeline showing the failures and passes of all my CI jobs for this specific salt formula
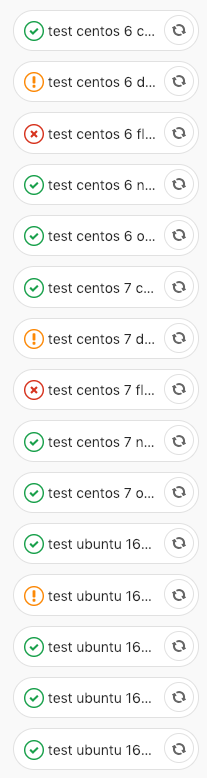
All 23 comments
Just to update this, here's some diagnostics data from a VM, and running the same stuff without going onto the CI machines itself. Taking GitLab, and it's CI mechanism out of the question
Below is the output from CentOS 7
[root@salt-kitchen-06 ~]# kitchen login flourine-centos-7
Last login: Thu Jan 31 17:38:44 2019 from gateway
[kitchen@fca24d9d85ee ~]$ sudo su -
Last login: Thu Jan 31 17:39:04 UTC 2019 on pts/0
[root@fca24d9d85ee ~]# salt-call grains.get virtual --local
local:
physical
[root@fca24d9d85ee ~]# salt --version
salt 2019.2.0-n/a-a16461b (Fluorine)
[root@fca24d9d85ee ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.6.1810 (Core)
And below is the output from Ubuntu
[root@salt-kitchen-06 ~]# kitchen login flourine-ubuntu-1604
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.5 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.10.0-862.11.6.el7.x86_64 x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
Last login: Thu Jan 31 17:45:21 2019 from 172.17.0.1
kitchen@5e22aafd61ed:~$ sudo su -
root@5e22aafd61ed:~# salt-call grains.get virtual --local
local:
kvm
root@5e22aafd61ed:~# salt --version
salt 2019.2.0-n/a-a16461b (Fluorine)
root@5e22aafd61ed:~# cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 16.04.5 LTS \n \l
I would expect to see kvm on both
@arif-ali thanks for reporting this. We will look into it.
On these systems do you have the virt-what binary installed? We change how we get this value if that is present because it can give us a more accurate reading. If you can let me know if the output changes with this installed of not it will help us a great deal.
As we dive in deeper we will likely also ask you to see if certain files are present.
@thatch45 thanks for that, ok indeed, by installing virt-what it does solve the problem. But we can't expect people to normally install that on all their machines.
Unless you have this as a planned dependency on the RPM/DEB packages when the package is finally available? Obviously, at the moment, I am grabbing fluorine via git
@gtmanfred is it worth having this dependency installed as part of salt_solo in kitchen-salt?
I was mostly asking about virt-what to help us diagnose the issue, we certainly need to fix it, but this allows us to better zone in on the code with the issue.
ah, ok, no problems. I thought it was a new dependency :)
Let me know if you need anything else, and I'll happily assist
Will do, thanks!
So, after adding virt-what into all my docker images, and adding it to my internal GitLab registry, I merged my local changes, thinking, that adding this package will temporarily resolve the problem. However, now everything passes, except for Ubuntu 16.04 with carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. Ubuntu 16.04 passes for fluorine though.
Any thoughts?
That makes me wonder if it is a virt-what bug, can you tell us what you see when you run virt-what directly?
But we have very extensive checks around virtualization, and we look for a lot of commands to run for the checks, I am wondering if this is because the container you are is is just too stripped down?
Here is the detection code:
https://github.com/saltstack/salt/blob/develop/salt/grains/core.py#L677
So virt-what does give the same information no matter what, but the code that you have linked to is from develop/fluorine, as shown below
lxc
kvm
So for fluorine, it works fine, I need to figure out what the issues are in oxygen, carbon and nitrogen for the OSs, and look at the corresponding code
Just going through all the steps of that code
Below are the commands that it uses in the order that it finds it.
- systemd-virt-detect
- virt-what -- doesn't exist by default
- dmidecode
- lspci -- doesn't exist by default
Below are the outputs of these commands, as the ones available by default
systemd-virt-detect
# for kitchen in `kitchen list | grep nitrogen | awk '{print $1}'`; do kitchen exec $kitchen -c "sudo systemd-detect-virt"; done
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-centos-6.
sudo: systemd-detect-virt: command not found
>>>>>> ------Exception-------
>>>>>> Class: Kitchen::Transport::SshFailed
>>>>>> Message: SSH exited (1) for command: [sudo systemd-detect-virt]
>>>>>> ----------------------
>>>>>> Please see .kitchen/logs/kitchen.log for more details
>>>>>> Also try running `kitchen diagnose --all` for configuration
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-centos-7.
docker
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-ubuntu-1604.
docker
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-ubuntu-1804.
docker
dmidecode
# for kitchen in `kitchen list | grep nitrogen | awk '{print $1}'`; do kitchen exec $kitchen -c "sudo dmidecode | grep Manufacturer"; done
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-centos-6.
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-centos-7.
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-ubuntu-1604.
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
Manufacturer: QEMU
-----> Execute command on nitrogen-ubuntu-1804.
sudo: dmidecode: command not found
>>>>>> ------Exception-------
>>>>>> Class: Kitchen::Transport::SshFailed
>>>>>> Message: SSH exited (1) for command: [sudo dmidecode | grep Manufacturer]
>>>>>> ----------------------
>>>>>> Please see .kitchen/logs/kitchen.log for more details
>>>>>> Also try running `kitchen diagnose --all` for configuration
You may want to move the virt-what command stuff before the systemd-virt-detect, which will ensure that you get the correct results? does that make sense?
I am not saying this is what we need to do, but hopefully the above gives us a bit more info to solve the problem
@arif-ali I'm having a heck of a time reproducing this.
# bundle exec kitchen login flourine-centos-7
Last login: Wed Apr 3 21:19:26 2019 from gateway
[kitchen@8fb28780fd13 ~]$ sudo salt-call --local grains.get virtual
local:
bhyve
I'm using this kitchen.yml:
---
driver:
name: docker
platforms:
- name: centos-7
driver_config:
image: registry.ocf.co.uk/salt/docker/centos-7-kitchen:base
privileged: True
run_command: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd
use_cache: False
remove_images: True
provisioner:
salt_yum_repo: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/$releasever/$basearch/%s'
salt_yum_rpm_key: 'https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/7/x86_64/latest/SALTSTACK-GPG-KEY.pub'
salt_install: yum
provisioner:
name: salt_solo
salt_install: bootstrap
salt_version: latest
salt_bootstrap_options: -P -p git -p curl -p sudo git %s
formula: srv/salt
log_level: debug
sudo: true
require_chef: false
remote_states:
name: https://github.com/waynesaltdebugging/stay-t.git
branch: master
repo: git
testingdir: /testing
salt_copy_filter:
- __pycache__
- '*.pyc'
- .bundle
- .tox
- .kitchen
- artifacts
- Gemfile.lock
state_top:
base:
'*':
- boop
suites:
- name: flourine
provisioner:
salt_version: '2019.2'
salt_install: bootstrap
I wonder though - my docker version is:
Docker version 18.09.2, build 6247962
using Docker on Mac.
Are you still having this problem at all?
@arif-ali are you still seeing this issue?
Sorry, been on holiday, I will double check things. I worked around the problem by installing the extra packages in the docker containers myself as part of my own build process.
Just checked your kitchen.yml. That will now work always, as the new docker containers that I have on our registry were fixed with the additional packages.
I will let you know how to replicate the issue when I get back to this
Hi @waynew,
I know this is an edge case, but an issue nevertheless.
So to replicate the issue, and this is how it's being run in our CI environment. I was only able to run this in a linux environment, it seems to pass where the underlying OS is MacOS. I then created a Ubuntu 18.04.2 VM, and I was able to mimic the issue as shown below. I also changed the image line to be centos:7 instead of registry.ocf.co.uk/salt/docker/centos-7-kitchen:base
docker run --privileged --name df-docker -d docker:dind
docker run --rm -it --link df-docker:docker docker sh
apk add ruby-dev ruby-bundler gcc libc-dev make py2-pip python2-dev git openssh
cd /root
git clone <url/to/your/formula/>
cd <to/folder/of/formula>
bundle install
kitchen converge flourine-centos-7
Then to test, in the same manner as you have, I then did the following
# bundle exec kitchen login flourine-centos-7
Last login: Fri Apr 12 19:44:37 2019 from 172.17.0.3
[kitchen@c2d40272abd1 ~]$ sudo salt-call --local grains.get virtual
local:
physical
I hope that makes sense
@arif-ali ah excellent, I'll give that a shot and see if I can repro
Huh. When I try to follow your instructions it fails on the converge step.
/salt # bundle exec kitchen converge flourine-centos-7
bundler: failed to load command: kitchen (/usr/bin/kitchen)
TypeError: no implicit conversion of nil into String
/usr/lib/ruby/gems/2.5.0/gems/rbnacl-libsodium-1.0.16/lib/rbnacl/libsodium.rb:22:in `join'
<snip>
However, I did get it installed under Docker under Vagrant, and the grains.get virtual showed VirtualBox. On a normal docker under Mac I get bhyve.
Well, that was even easier than that. Just this:
docker run --privileged --name df-docker -d docker:dind
docker run --rm -it --link df-docker:docker docker sh
docker run --rm -it centos:7
curl -Lo bootstrap.sh https://bootstrap.saltstack.com
chmod +x bootstrap.sh
./bootstrap.sh -X
salt-call --local grains.get virtual
In fact, you don't even need to do that:
docker run --privileged --name df-docker -d docker:dind
docker run --rm -it --link df-docker:docker docker sh
apk add curl openrc
curl -Lo bootstrap.sh https://bootstrap.saltstack.com
chmod +x bootstrap.sh
./bootstrap.sh -X
salt-call --local grains.get virtual
And, even that is more - just installing salt on the docker, or alpine image, grains.virtual shows up as physical. Oh, huh. Interesting. So, it looks like it's actually just failing to set the grains['virtual'] = '???' inside an alpine linux container.
@arif-ali Can you give your attempt a retry, but also check grains.get virtual_subtype? I'm pretty sure that what you'll see is that the virtual grain is physical and the virtual_subtype grain is Docker. Which makes no sense and is clearly a bug 😂
here's my full transcript
https://gitlab.ocf.co.uk/snippets/94
Below is the final output of both virtual and virtual_subtype
[kitchen@41f459c85e8b ~]$ sudo salt-call --local grains.get virtual
local:
physical
[kitchen@41f459c85e8b ~]$ sudo salt-call --local grains.get virtual_subtype
local:
Docker
Perfect, thanks!
@arif-ali if you are in a position where you can, feel free to try the fix in my PR
@waynew, I have tested this using your particular branch as well as 2018.3, where it was merged to, and works without a problem. However, it will also need to be ported to 2019.2, which is where I was originally having the problem
@arif-ali Excellent!
Our merge forward process should certainly get it there. @Ch3LL / @garethgreenaway is there anything special that I need to do to make sure my fix is in a merge forward?
@waynew Nothing you need to do if you only need it into the 2019.2 branch. It will not get merged forward into the 2019.2.1 branch though. If you need it to get into the 2019.2.1 release you either need to cherry pick your fix into that branch or add the 2019.2.1 and Bugfix - back port labels to it and either gareth or I will cherry pick it. (i know technically its not a back port but that the label we check twice a week to see what needs to be backported/cherry picked)