Graphql-engine: Handling HTTP 400 inside a Hasura Action with .NET Core webhook
My organization is experimenting with Hasura Actions and we're using version 1.2.0-beta.4. The Action uses a .NET web service. My requests are being authored and sent from GraphiQL. Hasura and the .NET web services are being run in separate Docker containers.
When the data submitted to the web service is valid, everything works as expected. However, if the web service deems there is a validation error, it sends back an HTTP 400 with the following JSON:
{
"type":"https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-6.5.1",
"title":"One or more validation errors occurred.",
"status":400,
"traceId":"|1a5f0fdf-40225dbff4a6753d.",
"errors":{
"$.input.cosponsor_info.cosponsorDate":[
"The JSON value could not be converted to System.DateTime. Path: $.input.cosponsor_info.cosponsorDate |
LineNumber: 0 | BytePositionInLine: 126."
]
}
}
Inside of Hasura's GraphiQL, the error appears as:
{
"errors": [
{
"extensions": {
"path": "$",
"code": "parse-failed"
},
"message": "webhook response: the key 'message' was not present"
}
]
}
My guess is that the key under errors in the HTTP response ($.input.cosponsor_info.cosponsorDate) is causing a problem in basic parsing. But Microsoft indicates this style of response from .NET is being done according to some spec and is quite intentional and changing it seems to be no simple matter. The Hasura logging is also a little confusing at this point because it seems to indicate that it received HTTP 200. Here is the log entry from Hasura:
{
"type":"http-log",
"timestamp":"2020-04-22T13:21:58.118+0000",
"level":"error",
"detail":{
"operation":{
"user_vars":{
"x-hasura-role":"admin"
},
"error":{
"path":"$",
"error":"webhook response: the key 'message' was not present",
"code":"parse-failed"
},
"request_id":"baef50e0-a2d9-4b28-a907-6924733dc3c8",
"response_size":96,
"query":{
"query":"mutation {\n addCosponsorAction(cosponsor_info: {\n cosponsor: 523\n bill: 201\n sequence: 5\n cosponsorDate: \"4/15/20\"\n }) {\n errors\n }\n}\n"
}
},
"http_info":{
"status":200,
"http_version":"HTTP/1.1",
"url":"/v1/graphql",
"ip":"172.20.0.1",
"method":"POST",
"content_encoding":null
}
}
}
Here is the Action definition:
type Mutation {
addCosponsorAction (
cosponsor_info: addCosponsorActionInput!
): addCosponsorActionOutput
}
input addCosponsorActionInput {
cosponsor : Int!
bill : Int!
sequence : Int!
cosponsorDate : Date
}
scalar Date
type addCosponsorActionOutput {
data : String
status : Int
}
At one point I tried incorporating the JSON keys in the .NET error response into addCosponsorActionOuput, but that didn't change the error message.
And mutation being sent from GraphiQL:
mutation {
addCosponsorAction(cosponsor_info: {
cosponsor: 523
bill: 201
sequence: 5
cosponsorDate: "4/15/20"
}) {
data
status
}
}
I'm still rather new to GraphQL and Hasura so I'm hoping I'm missing something when it comes to handling these exception messages generated from .NET. Thanks in advance.
All 4 comments
Hi @crosseyedalien
Thanks for reporting this and also this issue.
It does appears that some default .NET thing is happening that Hasura has trouble parsing. Do you think we can get on a call and resolve these issues? It would also help us understand and improve support for .NET handlers. My email is [email protected].
Hey, updating with a solution for this:
There are two things you need to do in order to get .NET Core 3.1 to let you give custom error formats.
- Disable
ModelStateInvalidinApiBehaviorOptionsfrom inside ofConfigureServices():
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddScoped<ProductsRepository>();
services.AddDbContext<ProductContext>(opt =>
opt.UseInMemoryDatabase("ProductInventory"));
// This is needed to prevent the default Validation error ProblemDetails from returning
services.AddMvc()
.ConfigureApiBehaviorOptions(opt =>
{
opt.SuppressModelStateInvalidFilter = true;
});
}
- Write a method in
Configure()forapp.UseExceptionHandler()as a middleware/handler for catching + formatting exceptions:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
// Hasura Actions error-handler middleware, formats to spec-compliant output
app.UseExceptionHandler(a => a.Run(async context =>
{
var feature = context.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerPathFeature>();
var exception = feature.Error;
var result = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new
{
message = exception.Message
});
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(result);
}));
// Alternative - using GlobalExecptionHandler package from Nuget:
// https://github.com/JosephWoodward/GlobalExceptionHandlerDotNet
// app.UseGlobalExceptionHandler(x =>
// {
// x.ContentType = "application/json";
// x.ResponseBody(ex => JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new
// {
// Message = "An error occurred whilst processing your request"
// }));
// x.Map<ArgumentException>().ToStatusCode(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest).WithBody((ex, context) => JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new
// {
// message = ex.Message,
// }));
// });
// app.Map("/error", x => x.Run(y => throw new Exception()));
(...rest of code)
}
Here we just strip everything from the exception besides message (I wasn't sure how to get status code in there, and it's optional):
// Hasura Actions error-handler middleware, formats to spec-compliant output
app.UseExceptionHandler(a => a.Run(async context =>
{
var feature = context.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerPathFeature>();
var exception = feature.Error;
var result = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(new
{
message = exception.Message
});
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json";
await context.Response.WriteAsync(result);
}));
Updating with a better answer, using filters:
ResponseFilter.cs
using System.Net;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Filters;
public class ResponseFilter : IActionFilter {
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext context) { }
public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext context) {
if (context.Exception != null) {
var payload = new {
message = context.Exception.Message,
code = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError
};
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest;
context.Result = new JsonResult(payload);
context.ExceptionHandled = true;
} else if (context.Result is ObjectResult objectResult) {
var status = (int)objectResult.StatusCode.GetValueOrDefault(200);
switch (status) {
case (int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest:
case (int)HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized:
case (int)HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError:
case (int)HttpStatusCode.NotFound:
context.HttpContext.Response.StatusCode = status;
context.Result = new JsonResult(new {
message = (string)objectResult.Value,
code = status
});
break;
}
}
}
}
Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
// This is needed to prevent the default Validation errors from returning
services.AddMvc()
.ConfigureApiBehaviorOptions(opt => {
opt.SuppressModelStateInvalidFilter = true;
});
services.AddControllers(options =>
options.Filters.Add(new ResponseFilter()));
// ... (rest of code)
}
Sample Controller Endpoint (note the return on BadRequest):
[HttpPost]
[Consumes(MediaTypeNames.Application.Json)]
[ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status201Created)]
[ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest)]
public async Task<ActionResult<Product>> CreateAsync(Product product)
{
if (product.Description.Contains("XYZ Widget"))
{
return BadRequest("Not an acceptable description");
}
await _repository.AddProductAsync(product);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(GetById), new { id = product.Id }, product);
}
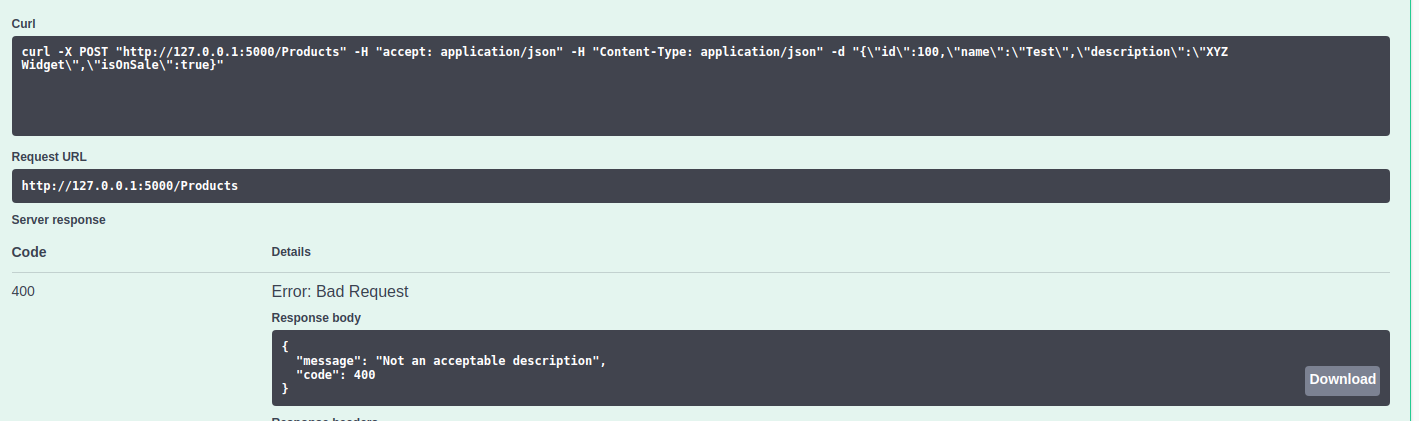
Here's some examples of the filter in use, with .NET Core 3.1 Swagger API extension:
Schema:
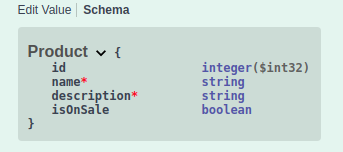
Model Validation ProblemDetails Error (Description as Int):

Return BadRequest() (Description as "XYZ Widget", code example from above):
Thanks! We made some minor adjustments for our environment, but this solves the problem.
Most helpful comment
Thanks! We made some minor adjustments for our environment, but this solves the problem.